
(PDF) A cadaveric study of the Arcade of Frohse
The arcade of Frohse, the leash of Henry, and the entire supinator muscle should be divided to relieve PIN compression. The incision for the brachioradialis-splitting approach is slightly more anterior over the mobile wad. The brachioradialis fascia is divided, and muscle fibers split bluntly, gaining access to the supinator and PIN.

IP Innovative Publication Pvt. Ltd
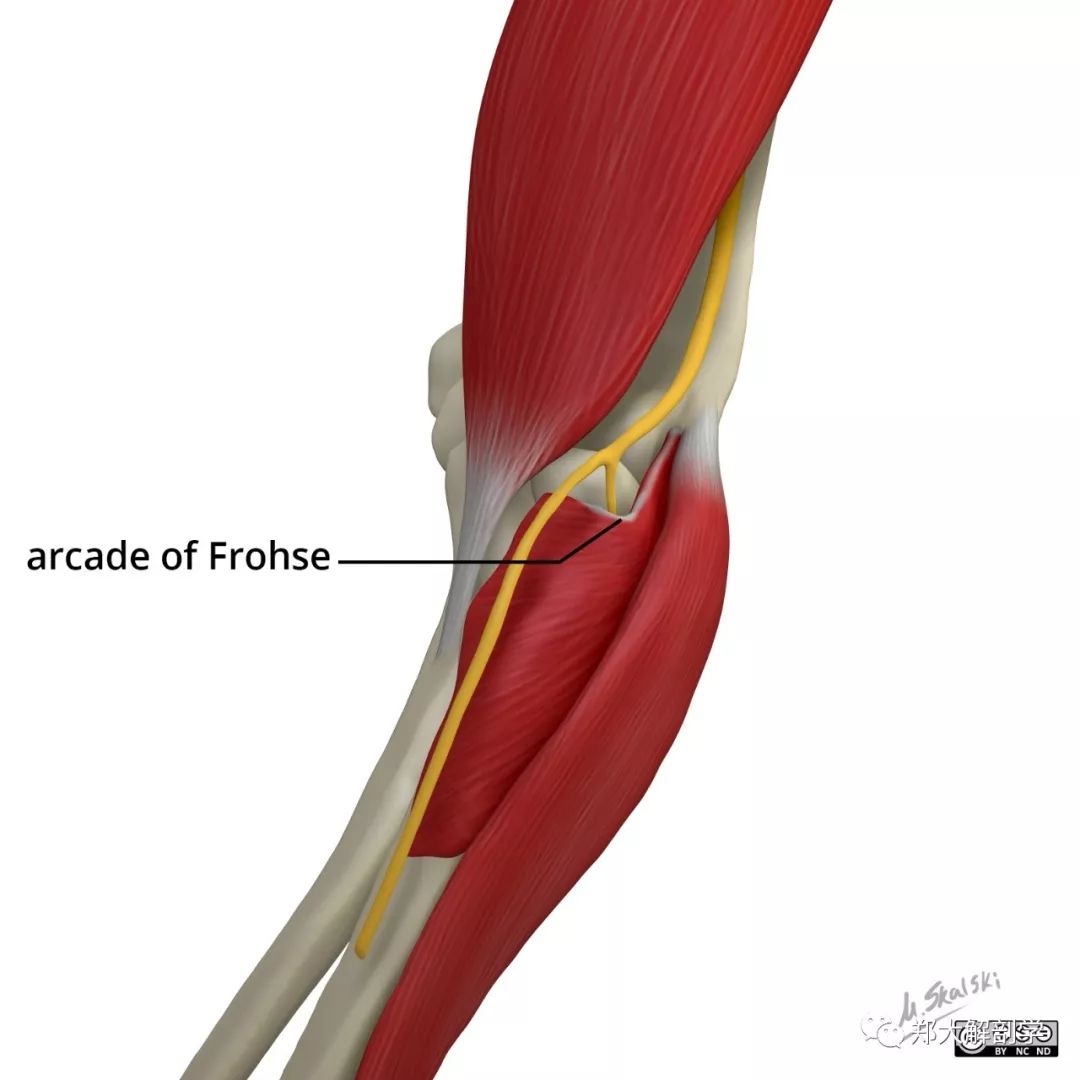
The arcade of Frohse is a commonly found structure in adults and thoughtful knowledge of its texture and morphology is especially useful in neurology, neurosurgery, orthopedics, trauma surgery and hand surgery, because it is considered to be the most common source of compression for the deep branch.

Arcade of Frohse YouTube
The arcade of Frohse is a commonly found structure in adults and thoughtful knowledge of its texture and morphology is especially useful in neurology, neurosurgery, orthopedics, trauma surgery and hand surgery, because it is considered to be the most common source of compression for the deep branch of the radial nerve. The structure of the proximal margin of the superficial layer of the.

PIN Compression Syndrome Hand Orthobullets
On physical exam, the patient has weakness of extension of the digits and wrist. Five potential sites of compression of the posterior interosseous nerve have been identified (7a,8a). Of these, the proximal tendinous edge of the supinator muscle (arcade of Frohse) is the most frequent site of posterior interosseous nerve entrapment (7a,8a) 2.

Radial Tunnel Syndrome — ChiroUp
Pathology. It is a result of posterior interosseous nerve compression from trauma, micro-trauma, space-occupying lesions or inflammation. The most commonly described sites of compression are the arcade of Frohse and the distal edge of the supinator muscle respectively 2.Other potential sites (proximal to distal) are: fibrous bands anterior to the radiocapitellar joint

Anatomy arcade of Frohse by posterolateral surgical approach
We identified the Frohse arcade with a well-developed fibrous constitution in 22 of the 30 dissected limbs (73%) and of muscular constitution in 8 (27%). The distal margin of the supinator muscle.

Posterior Interosseous Nerve Injury to The Incarcerated forearm Dr
The arcade of Frohse is the most common site of compression and represents a thickened tendinous proximal edge of the superficial head of the supinator, whereas the normal edge is thin and membranous. The tendinous thickening is developmental, occurring in 30-100% of people, most likely due to repetitive pronation-supination .

Figure 2 from Posterior Interosseous Nerve Palsy Caused by a Ganglion
This is most common at the arcade of Frohse, a tendinous arch formed by the proximal edge of the superficial head of the supinator muscle (the course of the radial nerve through the arcade of Frohse is shown in Fig. 6). Repeated pronation and supination are suggested to induce a fibrotic process which impinges the nerve between the arcade of Frohse and the proximal radius.

The drawing provides an anterior view of the course of the radial nerve
These sites include the radial head, the Leash of Henry (recurrent radial vessels), the arcade of Frohse, and the tendon of the extensor carpi radialis brevis . Repetitive pronation and supination are also associated with radial nerve entrapment . 1.5. Pathophysiology. Radial nerve injury typically occurs due to compression, entrapment.

Figure 1 from Crosssectional sonographic assessment of the posterior
Radial Tunnel Syndrome is a compressive neuropathy of the posterior interosseous nerve (PIN) at the level of proximal forearm (radial tunnel). Diagnosis is made clinically with pain only (maximal tenderness 3-5 cm distal to lateral epicondyle) without any motor or sensory dysfunction. Treatment is a prolonged course of conservative management.

Posterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome (Arcade of Frohse) YouTube
Near the bifurcation, the arcade of Frohse is released, potential compressive recurrent radial vessels are ligated, and the supinator muscle is released . Regardless of the approach used, the three different areas of constriction most frequently released are the arcade of Frohse, the distal edge of the supinator, and the recurrent radial artery if necessary.

The arcade of Frohse a systematic review and metaanalysis Request PDF
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. The arcade of Frohse (pronounced "\ˈfʁoːzə \") is also known as the supinator arch. The arcade is formed by a fibrous band between the two heads of the supinator muscle. The deep branch of the radial nerve passes beneath the arcade accompanied by vessels known as the leash of Henry.

Ultrasound scanning for Arcade of Frohse YouTube
arcade of Frohse, distal edge of supinator. Radial nerve compression occurs in throwing and overhead activities. Repetitive pronation and supination can also cause similar symptoms. It is important to examine the cervical spine and the radial nerve both proximal and distal to the elbow. It has been postulated that a proximal compression can.
胫神经,股,踝管(第2页)_大山谷图库
The posterior interosseous nerve may be compressed at multiple points along its course, most commonly under the arcade of Frohse, the fibrotendinous proximal edge of the supinator muscle. The nerve may also become compressed at the distal edge of the supinator muscle or under the medial edge of the extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle.

大拇指无力—可能是骨间后神经卡压综合征 (PIN) 知乎
The PIN enters the radial tunnel underneath a musculo-tendinous arch, the arcade of Frohse. Formed by the upper free border of the superficial head of the supinator, the arcade of Frohse is a semicircular fibrous arch that remains fibrous medially and is found in 30-80% of anatomical specimens (Spinner, 1968, Clavert et al., 2009).

The Elbow in Clinic. Elbow pain can have different causes… by Wayne C
The arcade of Frohse. The AF is not a homogenous structure; its shape and the type of fibers are variable. Debouck and Rooze proposed a classification of the arcade based on its morphology . Type A indicates a resistant tendinous arcade. Type B is a mixed musculotendinous arch with two types of fiber alternating.